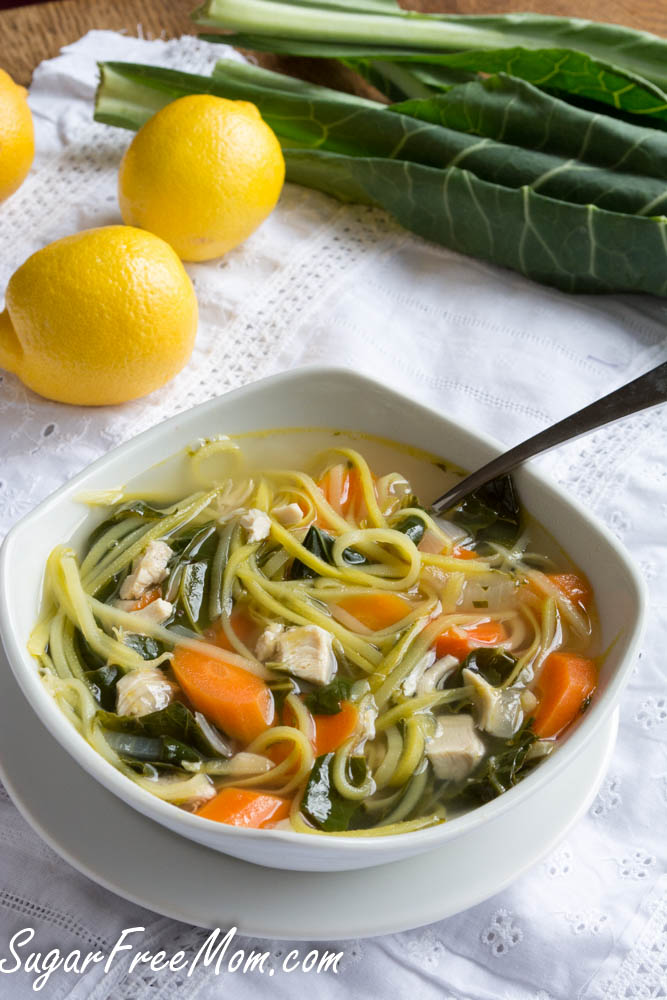
Over 95% of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as dioxins and PCBs comes from fish, other meats and dairy products.
The incidence of food-borne diseases can be “significantly reduced” as can be exposed to antibiotics, “pesticides, arsenic, dioxins, and hormones associated with traditional meat” by directly cultivating muscle meat without related organs like the intestines. Currently, the US Food and Drug Administration has approved seven hormone drugs to enhance milk and meat production. “In the European Union, such use is completely prohibited.” However, even if the hormones are not injected, animal products naturally carry the hormones to come from the animal. “Eggs given the example contribute to the dietary intake of estradiol (estrogen) than beef, whether the animal is legally treated with hormones or not.” After all, eggs come straight from the chicken’s ovaries, so of course they are swimming with the hormones. However, if you are growing only muscle meat or egg white protein directly, you do not need to include the genitals, adrenal glands, or related hormones.
“Chemical safety is another concern for meat produced under current production systems.” There are chemical toxicants and industrial pollutants that accumulate in the food chain, such as pesticides, PCBs, heavy metals, and inflammatory agents, but there is no food chain with cultivated meat. With Zero Mercury, we were able to produce all the tuna we wanted.
When the World Health Organization determined that the processed meat was known human carcinogens and unprocessed meat, it was not talking about carcinogenic environmental pollutants. When researchers tested retail meat and tested the presence of “calculated 33 carcinogenic chemicals,” polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), organochlorine pesticides like DDT, and dioxin-like PCBs, and PCBs like dioxin, they concluded to limit the risk of maximum beef and pork intake, in order to reduce the risk of cancer.
Why grow meat when you can buy organic food? Surprisingly, “Organic meat consumption does not reduce the likelihood of carcinogenicity associated with persistent organic pollutants (POPs) intake.” Many studies have recently compared the presence of environmental pollutants in organic and traditional meat, and researchers have surprisingly found that organic meat is sometimes more contaminated. It’s not just organic beef. Higher levels were also found in pork and chicken.
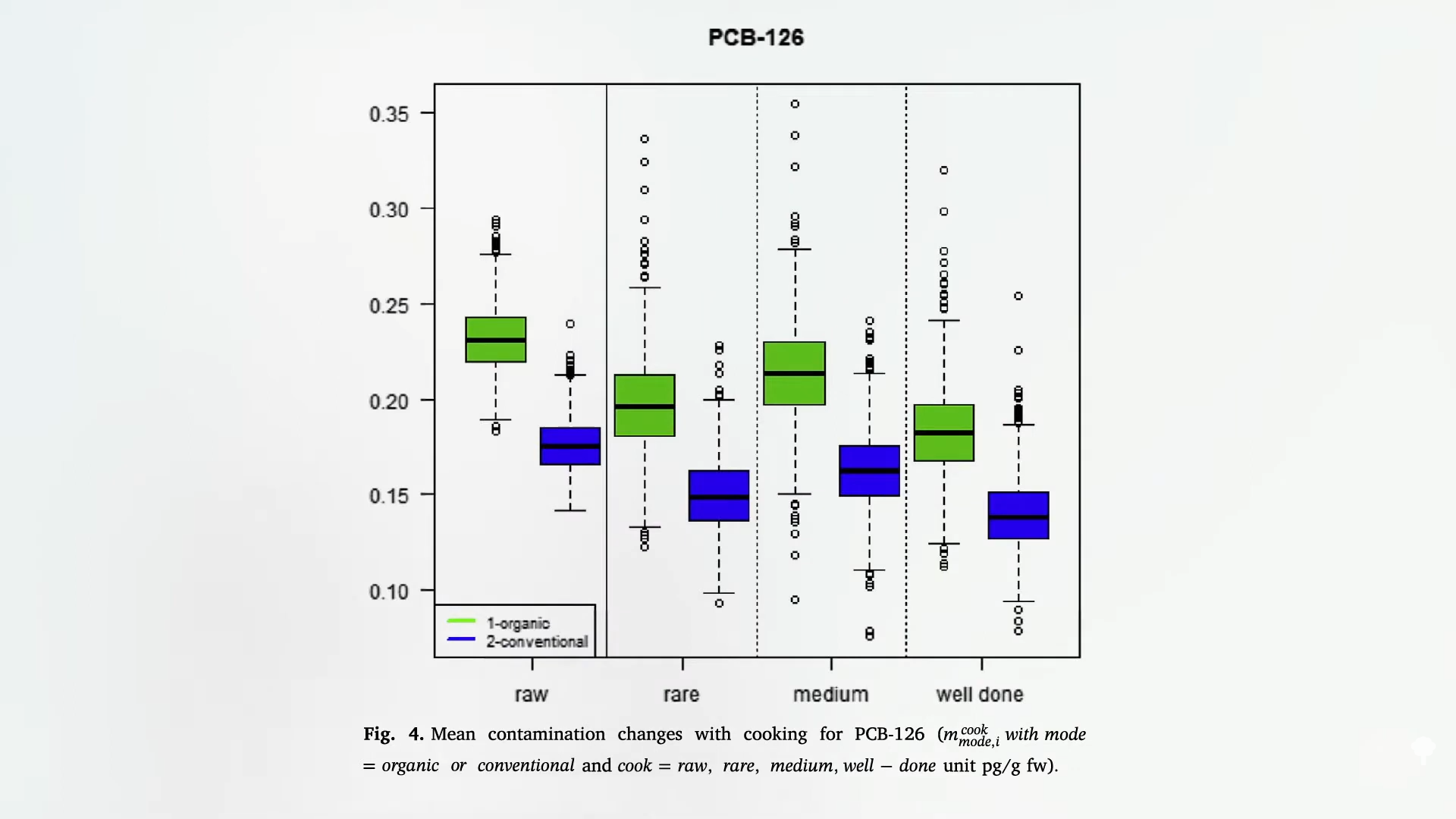
Looking at trace culates and chemical residues of both organic and traditional meat, several environmental contaminants such as dioxin, PCB, lead and arsenic were measured at significantly higher levels in organic samples. In my video, as shown below and at 2:56, the effects of cultivated meat on human health: chemical safety, green is organic meat, blue is traditional.
As shown here, cooking helps the PCB to pull out some of the fat that is concentrated, as shown at 3:01.
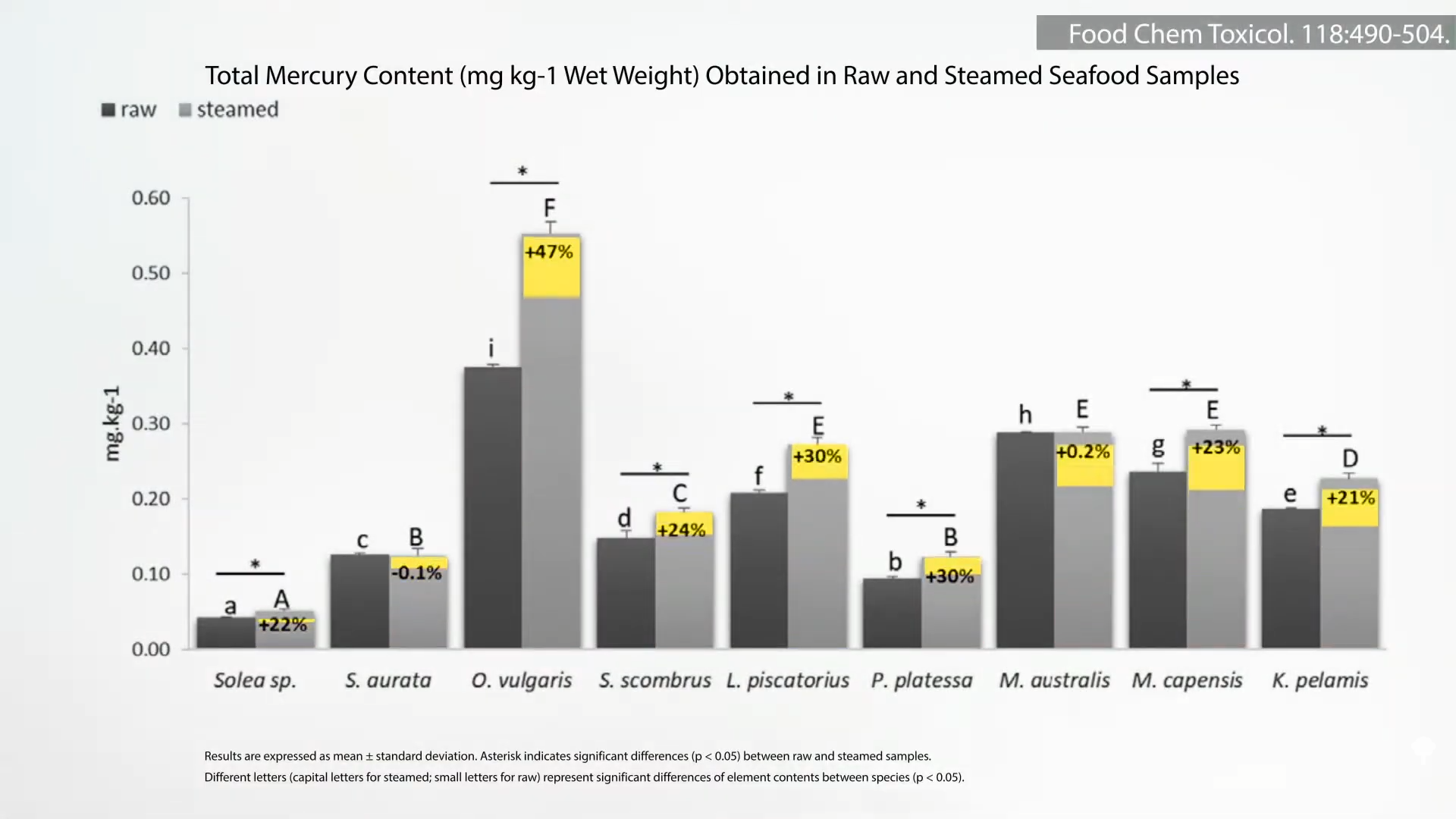
Seafood seems to be the exception. For example, steaming generally increases contaminant levels, increases contaminant exposure, and concentrates mercury levels as much as 47%, as can be seen here and at 3:15 in my video. It’s better not to have toxic buildups in the first place.
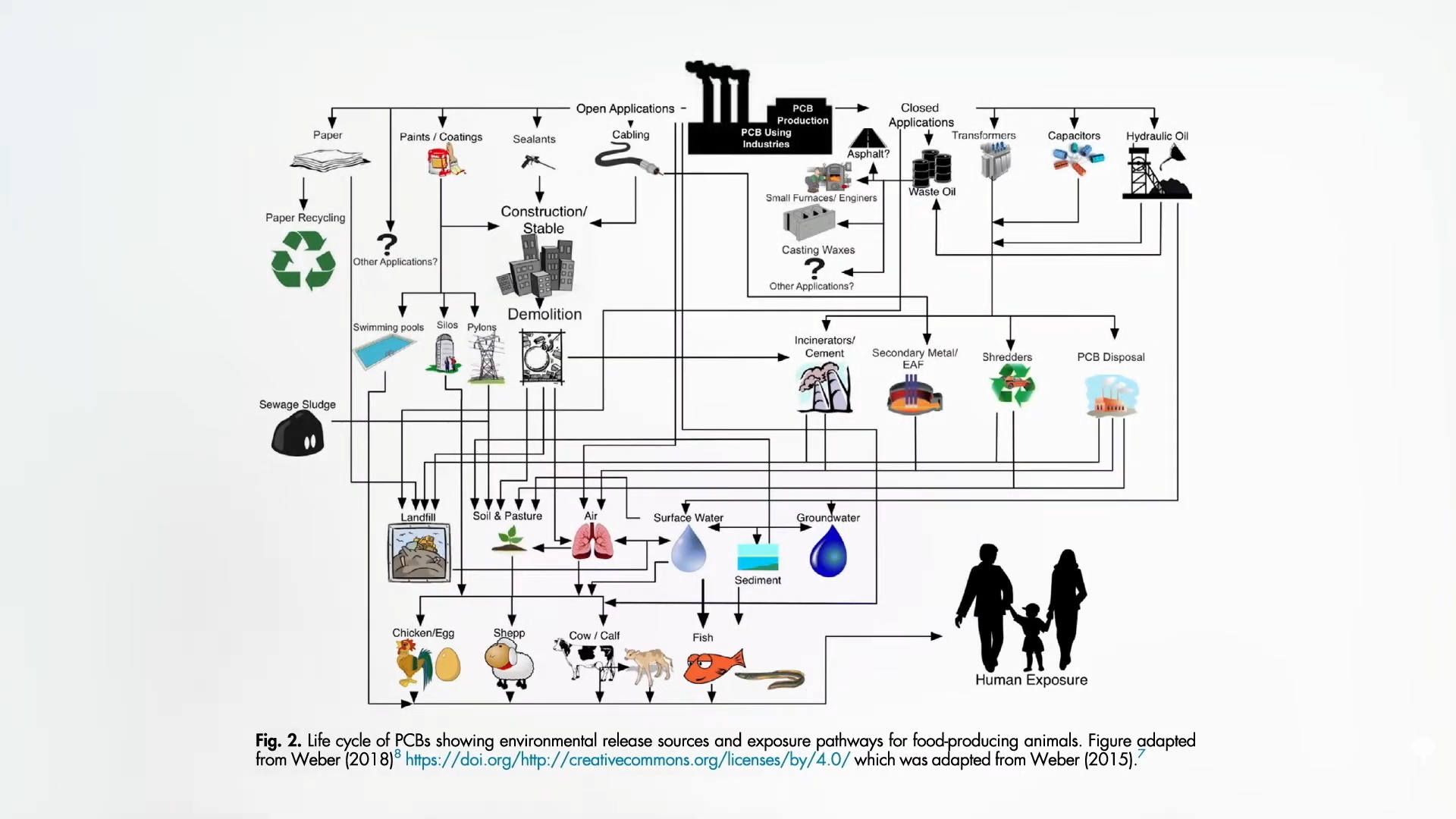
Over 95% of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as dioxins and PCBs come from foods like meat, including fatty fish and dairy products, but contaminants don’t look magical. The only way chicken, fish and other meat can lead to human exposure is because the animals themselves have built up lifelong exposure in contaminated worlds, such as incinerators, power plants, and sewage sludge, as you can see in my video.
Unlike traditional meat production, harvesting without slaughtering not only means there are no more infected animals, but there are no more contaminated animals. When it comes to pollutants, it’s like retrieving a time machine before the Industrial Revolution.
Doctor’s notes:
Cultivated meat means less contamination by fecal residues, toxic contaminants, antibiotics and hormones. Reduces environmental impact by up to 99%. There is zero pandemic risk. Cultivated meat also allows people to have their own meat and eat it without affecting the rest of us.
This is the final video for this cultivated meat series. If you missed the first two, check out our video on food safety and antibiotic resistance.
I previously did a video series about plant-based meat. See related posts below.
All videos from the Plant-Based Meat Series are also available in digital downloads from webinars I did. Look at the impact of plant-based and cultivated meat on human health for pandemic prevention and climate mitigation.